The growing interest in solar energy is driven by its multitude of environmental and economic benefits, making it an essential component in the fight against climate change and an increasingly attractive option for cost-conscious consumers. Harnessing the power of the sun, solar panels now play a pivotal role in both residential and commercial energy systems.
In this blog, we’ll illustrate everything you need to know about solar panels—from how they work to their benefits, installation, and future trends in solar technology.
What Are Solar Panels?
In simple terms, a solar panel is a device that captures sunlight and converts it into electricity. This process is accomplished through the use of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are designed to absorb solar radiation and generate an electric current. The electricity produced can be used immediately, stored in batteries, or fed into the grid for later use.
The fundamental technology behind solar panels enables them to perform a vital function: providing a clean and renewable energy source. By reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels, solar panels contribute to a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and help pave the way towards a more sustainable future.
Types of Solar Panels
Several types of solar panels are available on the market, each with its own unique characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks. The most common types include:
1. Monocrystalline Solar Panels:
- Description: Composed of pure silicon crystals, monocrystalline panels are recognized for their distinct, uniform appearance and high efficiency.
- Benefits: High efficiency, long lifespan, and better performance in low-light conditions.
- Drawbacks: Generally more expensive compared to other types.
2. Polycrystalline Solar Panels:
- Description: Made from silicon fragments rather than single crystals, these panels have a speckled blue appearance.
- Benefits: Lower cost, decent efficiency, and simpler manufacturing process.
- Drawbacks: Slightly lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline panels and slightly more space is required for installation.
3. Thin-Film Solar Panels:
- Description: These panels are created by layering thin sheets of photovoltaic material onto a substrate such as glass or metal.
- Benefits: Lightweight, flexible, and easy to integrate into various applications.
- Drawbacks: Lower efficiency and shorter lifespan compared to crystalline panels.
How Solar Panels Work
At the heart of solar energy generation is the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon discovered over a century ago by French physicist Alexandre Edmond Becquerel. Here’s a step-by-step look at how solar panels convert sunlight into electricity:
- Solar Energy Capture: When sunlight hits a solar panel, the energy from the light particles (photons) is absorbed by the silicon cells.
- Electrons Get Excited: Absorbed energy excites the silicon atoms, causing electrons to break free and move. This movement creates an electric current.
- Direct Current (DC) Generation: The current generated by the panels is direct current (DC), which flows in a single direction.
- Inversion to Alternating Current (AC): Since most household appliances and the electrical grid operate on alternating current (AC), an inverter is used to convert DC into AC.
- Grid Connection and Net Metering: The generated electricity is either used immediately, stored in batteries, or fed into the grid. Through net metering, surplus energy sent back to the grid can be credited, reducing future electricity bills.
What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy refers to the energy harnessed from the sun’s rays. The sunlight we receive on Earth is composed of photons, which are tiny particles of energy. Solar panels capture these photons and convert them into usable electricity.
The Photovoltaic Effect
The core technology behind solar panels is the photovoltaic effect, which occurs when photons hit a semiconductor material (typically silicon) and excite its electrons. This movement of electrons creates an electric current, which is then captured and transferred through the wiring of the solar panel for use as electricity.
Grid Connection and Net Metering
Most solar panel systems are connected to the local electrical grid, allowing for a seamless transition between solar and traditional energy sources. This is where net metering comes into play. Net metering allows homeowners to “sell” excess electricity generated by their solar panels back to the grid, effectively reducing their electricity bills.
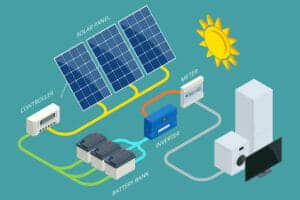
What Components Make Up a Solar System?
A typical solar power system consists of several key components that work together seamlessly:
- Solar Photovoltaic Panels: The primary element that captures and converts sunlight into electrical power.
- Inverters: Devices that convert the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) for household use.
- Racking and Mounting System: These structures securely attach the solar panels to rooftops or the ground, ensuring optimal positioning and stability.
- Solar Performance Monitoring Systems: These are software or devices that track the system’s performance, helping identify any issues and optimizing efficiency.
Benefits of Using Solar Panels
The adoption of solar panels offers numerous advantages, including:
- Cost Savings: By generating your own electricity, you can significantly reduce or even eliminate your electricity bills. Over time, solar panels can also protect you from rising energy costs.
- Environmental Impact: Solar energy is clean and renewable, producing zero emissions once operational. By switching to solar, you can drastically reduce your carbon footprint.
- Energy Independence: Owning a solar power system allows you to produce your own electricity, reducing reliance on external energy sources and increasing your energy security.
To illustrate the incredible potential of solar energy, consider this: an average solar power system can offset nearly 100,000 pounds of carbon dioxide in just 20 years—the equivalent of planting over 2,500 trees.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Efficiency
The efficiency of solar panels – how much sunlight they can convert into usable electricity – depends on several factors:
- Location: Geographic location determines the amount of sunlight received, influencing overall system efficiency.
- Angle: Solar panels should be positioned at the optimal angle to capture the most sunlight throughout the year.
- Shading: Shade from trees or nearby structures can substantially reduce panel efficiency.
- Temperature: Interestingly, extreme heat can cause solar panels to lose efficiency. An optimal temperature range is typically between 15°C to 35°C (59°F to 95°F).
Tips for Maximizing Efficiency
- Ensure your panels are installed at the appropriate angle for maximum sun exposure.
- Regularly trim any trees or vegetation that might cast shadows on the panels.
- Keep panels clean and free of dust or debris.
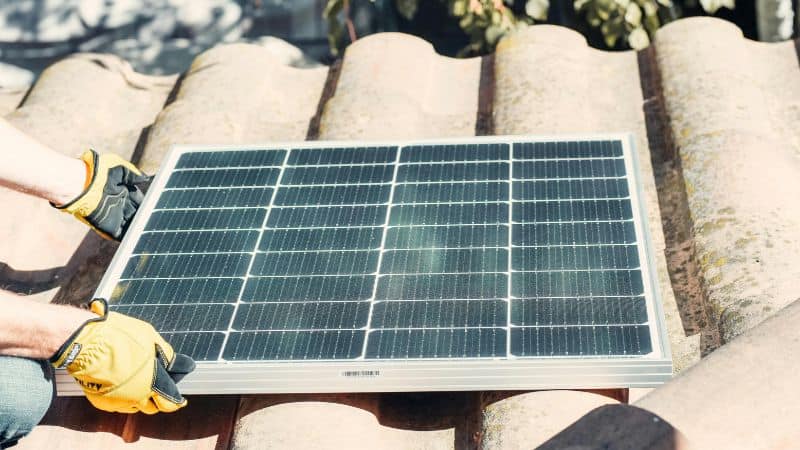
Installation Process
The installation of solar panels typically involves several steps:
- Assessment: A solar expert will evaluate your property to determine the best placement for your panels based on factors like sun exposure, roof condition, and available space.
- Design: After the assessment, a custom solar panel system will be designed to fit your specific needs and maximize energy production.
- Permits and Approvals: Before installation can begin, permits and approvals from local authorities are required. Your solar installer will usually handle this process.
- Installation: The actual installation of the solar panels typically takes one to three days depending on the size and complexity of the system.
- Connection to the Grid: Once installed, your system will be connected to the grid, and any necessary inspections will be performed to ensure everything is working correctly.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Solar panels are designed for durability and require minimal maintenance. However, to ensure optimal performance:
- Cleaning: Regularly clear panels of dust, leaves, and other debris.
- Inspection: Periodically have a professional check the system for issues or degradation.
Most solar panels come with warranties lasting between 20 to 25 years, but panels often continue to function well beyond that—potentially for 30 years or more.

Environmental Impact
The environmental benefits of solar panels cannot be overstated:
- Reducing Carbon Emissions: Solar panels generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, significantly reducing your carbon footprint.
- Less Reliance on Fossil Fuels: By using solar energy instead of traditional fossil fuels, you contribute to a reduction in the extraction, transportation, and burning of these non-renewable resources.
However, traditional energy sources such as coal and natural gas contribute heavily to air pollution and are major drivers of climate change. Solar energy, on the other hand, is a clean, renewable resource that can provide a virtually limitless supply of electricity without harming the environment.
Future of Solar Energy
The future of solar energy looks bright. Many exciting trends and innovations are emerging in the field:
- Improved Efficiency: Research is continually advancing the efficiency of solar panels, allowing them to generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight.
- Energy Storage Solutions: Battery technologies are improving, making it possible for homes to store solar energy for use during nights and cloudy days.
- Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Solar cells are being integrated into building materials like windows and roof tiles, allowing for more seamless and aesthetically pleasing solar energy solutions.
As innovation accelerates, we can expect solar technology to become even more efficient, accessible, and integrated into our daily lives.
Embrace the Solar Future with Deye
Solar panels offer an incredible opportunity to reduce energy costs, lower your carbon footprint, and gain independence from conventional energy sources. From understanding how solar panels work to knowing the benefits and installation process, we hope this blog has provided you with a comprehensive overview of solar energy and why it’s worth considering.
If you’re interested in exploring solar energy further, we encourage you to conduct additional research or consult with a solar energy expert. Tools and online calculators are available to help you estimate the benefits of installing solar panels on your property. Now is the perfect time to join the renewable energy revolution and make a positive impact on both your wallet and the planet. Consider Deye for your solar energy solutions. Our innovative products are designed to maximize efficiency and sustainability, guiding you every step of the way to ensure you get the most out of your solar investment. Let’s work together to create a brighter, greener future!